At the end of December 2023, I followed a training at scrum.org that related to Product Backlog Management (PBM).
The training called Professional Scrum Product Backlog Management Skills (PSPBM for short) is very practical and gives you tools to start straight away in the real world. As a nice addition, you can get certified for this and go into more depth through self-study.
The training has inspired me to write a blog in which a number of important aspects will be discussed.
What is Product Backlog Management
Product backlog management is a crucial aspect of agile development, helping teams prioritize and deliver valuable features efficiently.
Effective Product Backlog Management is about optimizing the flow of work, ensuring alignment with business goals, and fostering collaboration among team members to deliver a valuable and high-quality product. Central to Product Backlog Management are the role of the Product Owner and the artifact Product Backlog with associated (commitment) Product Goal.
Briefly, something about the product owner and the product backlog from the scrum guide:
Product Owner: is accountable for maximizing the value of the product resulting from the work of the Scrum Team. The Product Owner is also accountable for effective Product Backlog management, which includes:
- Developing and explicitly communicating the Product Goal.
- Creating and clearly communicating Product Backlog items.
- Ordering Product Backlog items.
- Ensuring that the Product Backlog is transparent, visible and understood.
The Product Owner may do the above work or may delegate the responsibility to others. Regardless, the Product Owner remains accountable.
Product Backlog : is an emergent, ordered list of what is needed to improve the product. It is the single source of work undertaken by the Scrum Team.
Apsects of Product Backlog Management
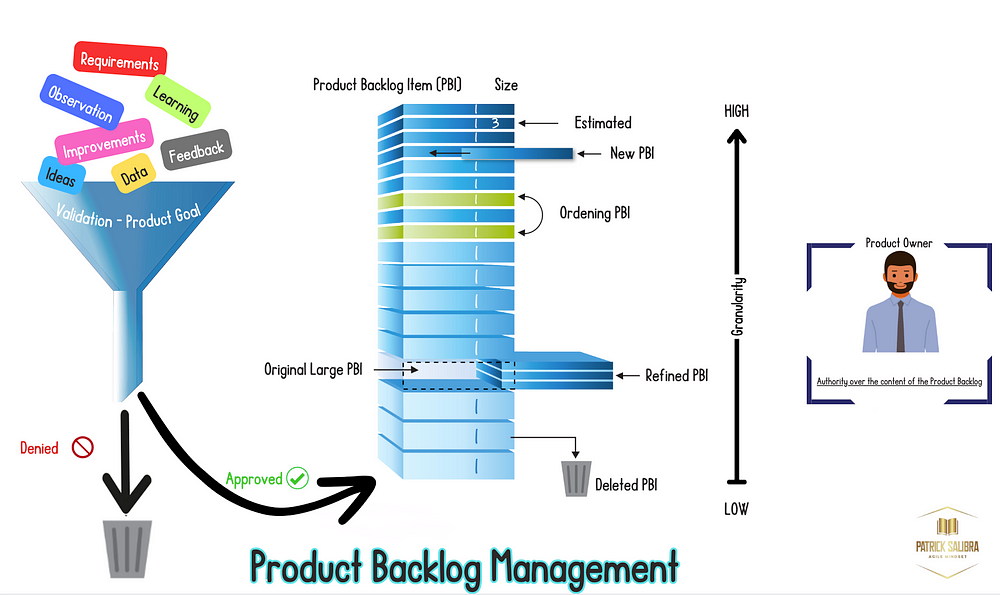
Using the image below and the associated numbers, we will go through a number of aspects of product backlog management:
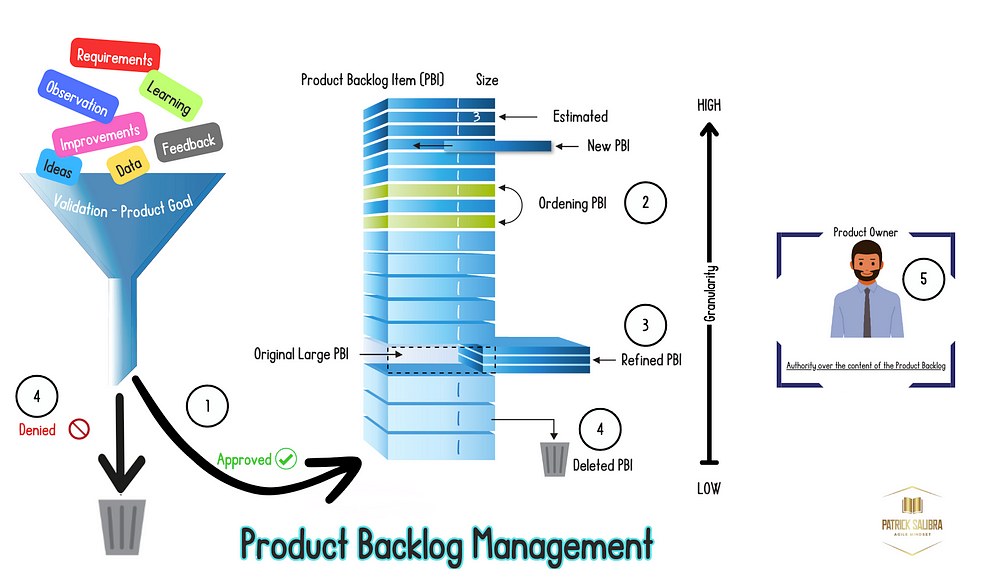
1 — Creation of Product Backlog or adding new PBI
- The product backlog is initiated during the project’s inception.
- It contains all the desired features, Improvements, Requirements, Learning, NFR’s, Enablers, etc etc that Scrum Team and Stakeholders envision for the product.

- PBI entered are in line and validated with Product Goal
2 — Ordering Product Backlog
- Value-driven: Prioritize items based on the value they bring to the customer and the business. This ensures that high-priority features are delivered early, maximizing the return on investment.
- Risk-based: Consider dependencies, technical risks, and market risks when prioritizing. Addressing high-risk items early in the backlog reduces uncertainties later in the project.

- High-priority items are usually placed at the top of the backlog.
- The product owner is advised by the scrum team and stakeholders, but as an authority he is the only one who determines the order
- There are various techniques to determine the ordering, such as Moscow, RICE, KANO, Value Poker, Magic Estimation, Buy a Feature, 35 etc etc. However, the product Owner is the one who determined which technique and the final order.
- Applying a certain technique of ordening is no guarantee that increment will deliver value. The real moment of assessment is when the increment is delivered to users and used by them
3 — Product Backlog Refinement
- Well-defined: PBI should be clear, concise, and understandable by all team members. Each story should represent a small piece of functionality that delivers value to the end user.
- Independent: PBI should be independent of each other, allowing for flexibility in prioritization and execution. This enables the team to work on the most valuable features first.

- Estimation: Each PBI is estimated in terms of effort or complexity. This helps the team understand the size of each task and aids in planning.
- Because PBI can be very broad, no specific format is really required. The standard here is that the team chooses the method itself and keeps in mind that it is transparent and clearly described.
- Regular Refinement: Set aside time for regular backlog grooming sessions to review and refine the backlog. This involves adding new items, removing irrelevant ones, and updating priorities based on changing business needs.
4 — Deleting PBI
- As a product owner you are continuously inspecting your Product Backlog to determine which PBI have value and determine if PBI are not relevant to remove them from the Product Backlog. This ensures a high degree of transparency in your product backlog

- Work that is not in line with the product goal is not included in the Product Backlog. As a product owner you sometimes have to say NO to keep focus on PBI that have values. Not including irrelevant information also ensures that the Product Backlog is transparent and easy to understand for Stakeholders and Scrum tTeam
5 — Product Owner
- Transparency: Keep stakeholders informed about the status of the backlog and any changes in priorities. This transparency helps manage expectations and aligns everyone involved in the project.
- Collaboration: Foster collaboration among team members, product owners, and stakeholders. Regular communication ensures that everyone is on the same page regarding the goals and priorities of the project.

- Use of metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as throughput, lead time, and cycle time. These metrics provide insights into the team’s performance and can be used to continuously improve the development process. Please realize that because we work in a complex environment, the above indicators do not guarantee future results
- Feedback loops: Establish feedback loops to gather insights from customers and end users. This information can be valuable for adjusting priorities and refining the backlog based on real-world usage and feedback.
Conclusion
Effective product backlog management requires a balance between flexibility and stability, with a focus on delivering value to the customer. Regularly reassess and adjust priorities based on feedback and changing business conditions to optimize the product development process.
Hopefully this blog has given you some more insights into the different aspects of product backlog management.
Resource
- Scrum Guide 2020
- Professional Scrum Product Backlog Management Skills™ Training
- Prioritization Techniques for the Product Owner
- 10 Tips for Effective Product Backlog Management
- https://www.youtube.com/embed/-mZO9aASfQA?si=VUQjnio3iRQPv_Au

